The Economic Contribution of Family Firms in the UK
Introduction
Family businesses are a cornerstone of the UK’s economy, playing a critical role across industries, regions, and communities. This research and policy briefing (#6 in the series) summarizes the key findings from the Family Business Research Foundation’s (FBRF) State of the Nation 2023 report, produced in collaboration with the Centre for Economics and Business Research (Cebr). The purpose of this briefing is to highlight the sector’s demographic profile and economic contributions in 2023, with the goal of providing actionable insights for policymakers, researchers, and stakeholders.
Methodology and Data Sources
The FBRF’s family-business sector report for 2023 employs multiple datasets to estimate the demographic and economic impact of family businesses in that year. Key data sources used to produce the estimates in the report include, for example:
The Longitudinal Small Business Survey (LSBS), conducted between 2023–2024, capturing data from UK firms with up to 250 employees.
The Business Population Estimates (BPE) for turnover, employment, and firm counts.
The Annual Business Survey (ABS) for sectoral Gross Value Added (GVA) and employee compensation figures.
Supplementary business demographic data from the Management and Wellbeing Practices Survey (MWPS) and the IFB Research Foundation’s study of large family firms (Repgraph, 2019).
Family businesses were defined according to the European Commission (2009) definition, and included sole proprietors, micro-businesses, and listed firms with significant family control.
The Economic Contribution of Family Businesses in the UK
Family businesses contributed significantly to the UK economy in 2023, across all regions, UK countries, and industries.
Cebr estimates that, in 2023, family businesses generated £2,805 billion in turnover, comprising nearly 50 per cent of private sector turnover. Despite being the group with the lowest prevalence of family ownership (29.7 per cent of businesses), large family businesses contributed the most to the sector’s turnover, having generated £974 billion in turnover in 2023.
Cebr estimates that family businesses supported a total of 15.8 million jobs in the UK in 2023, or 57 per cent of total private sector employment nationally. Micro family businesses (with and without employees)[1], were responsible for around half of this employment.
Micro family businesses without employees were the largest contributor to family business private sector employment supporting 4.4 million working proprietors, or 28 per cent of total family business employment. When excluding micro businesses without employees, total family business employment came down to a total of 11.3 million.
Employee compensation refers to total employment costs, or the total amount paid in compensation (including salaries, pensions, monetary benefits, etc.) by businesses. In 2023, family-owned businesses paid £401 billion in employee compensation, representing 45.7 per cent of the UK private sector total. Large businesses were the largest contributors to family business employee compensation, paying £151 billion to their employees, or 38 per cent of the family business total. Micro businesses with employees accounted for the smallest share of family business employee compensation (18 per cent), due mainly to their comparatively lower contributions to employee compensation (i.e. lower average wages) in the wider economy (Office for National Statistics, 2024).
Cebr estimate that family firms had a Total Tax Contribution (TTC) of £422 billion in 2023. The TTC methodology developed by PwC[2] is a measure of tax contribution that incorporates both taxes borne and taxes collected.[3] Cebr estimates that family firms contributed a total of £422 billion in taxation to the UK Exchequer in 2023 – of this, £142 billion was generated through taxes borne, and £280 billion through taxes collected. Family business TTC as a percentage of turnover was 17.5 per cent for 2023. By contrast, PwC estimated that, for 2021, TTC as a percentage of turnover for family businesses was 18.5 per cent (PwC/IFB Research Foundation, 2023).
Table 1 provides a summary of key statistics used to indicate the economic contribution of family-owned businesses in the UK in 2023.
Table 1: Key statistics showing the contribution
|
Indicator |
Contribution |
% of private sector |
|
Turnover (£bn) |
2,805 |
49.8% |
|
GVA (£bn) |
985 |
59.1% |
|
Employment (million jobs) |
15.8 |
56.9% |
|
Compensation of Employees (£bn) |
401 |
45.7% |
|
Total Tax Contribution (£bn) |
422 |
|
Family Business Demographics in the UK
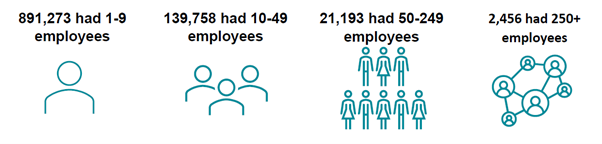
In 2023, Cebr estimate that there approximately 5.13 million family businesses in the UK, accounting for 93.2 per cent of all private sector firms, and 73.9 per cent of private sector firms with employees. While 79.4 per cent of family firms were micro-businesses without employees, only 0.1 per cent were large enterprises (250+ employees). Family businesses were prevalent in construction (833,188 firms), wholesale and retail (510,069), and professional services (709,311).
As previous studies by the FBRF have shown, family ownership varies with firm size – the smaller the business, the more likely it will be family-owned and run. In 2023, it is estimated that around 77 per cent of micro firms (1-9 employees) were family owned, compared with 30 per cent of large firms (more than 250+ employees) (Figure 1).
Figure 1: Family ownership among private businesses with employees by size, 2023
Sources: Department for Business and Trade (2024a), DBT (2024b), NIESR (2023), RepGraph (2020), Cebr analysis
Figure 2 shows the prevalence of family ownership across industries among family firms with employees. Family firms are most commonly found in the primary sector (which includes agriculture, mining, and utilities) and construction, and least likely to be found in arts, entertainment, and recreation, and health and social care.
Figure 2: Share of private businesses with employees that were family-owned by industry, %, 2023
*The “primary” sector covers agriculture, mining, and utilities. “Other service activities” cover services that are excluded elsewhere, such as trade unions, and religious and political organisations.
Sources: DBT (2024a), DBT (2024b), NIESR (2023), RepGraph (2020), Cebr analysis
Of the 5,126,505 family businesses in the UK, Cebr estimate that 4,467,190 were in England, 329,847 in Scotland, 206,248 in Wales, and 123,221 in Northern Ireland. In percentage terms, this is equivalent to 87.1 per cent being in England, 6.4 per cent in Scotland, 4.0 per cent in Wales, and 2.4 per cent in Northern Ireland.
In 2023, of the 5,126,505 family businesses in the UK, 1,054,680 were employers.
In Focus: Family Firms in the Wholesale and Retail Sector
The wholesale and retail trade sector contributed most to turnover and employment. This section presents key information about family firms in this important sector.
Demographics
The wholesale and retail trade sector had the third highest number of family businesses (including micro-businesses without employees) in 2023 with 510,069 firms. This represented 91.3 per cent of all firms operating in this sector.
It also had the greatest number of family businesses with employees in 2023 with 195,755 firms, amounting to 80.2 per cent of private businesses with employees operating in the wholesale and retail trade sector.
Economic Contribution
Turnover of family firms in the wholesale and retail trade sector in 2023 was £974bn, greater than any other sector. This equated to 53.8 per cent of all private sector turnover for businesses in this sector, and 34.7 per cent of total family business turnover.
Family firms in the wholesale and retail trade sector generated more GVA than family businesses in other sectors, Total GVA of family-owned businesses in this sector was £140bn, or 53.1 per cent of private sector GVA in this industry.
Family firms in this sector employed 2.73mn people, more than family firms in any other sector. This represented 68.4 per cent of all employment in businesses in the wholesale and retail trade sector.
Family firms in this sector made among the largest contributions to family business employee compensation, a total of £55,157mn, on average paying employees £24,339 per annum.
Conclusion
This research and policy research briefing summarizes some of the latest findings from the "State of the Nation: the UK Family Business Sector in 2023", underscoring the critical role family firms play in driving economic growth across the country. The report includes up-to-date information about the demographics of family-owned firms in the UK and offers new evidence to inform policy debates about the role of family businesses in the economy and the impact of recent changes in UK taxation policy on family-owned businesses.
The full report can be downloaded here.
Notes
[1] For consistency with the source data, micro businesses without employees are treated here as firms with one employee. This is because the Business Property Estimates (BPE) counts working proprietors as contributing to overall employment (Department for Business and Trade, 2024a).
[2] See PwC/IFB Research Foundation (2023)
[3] Total Tax Contribution considers both taxes borne (direct business payments to the government, such as corporation tax, employers’ national insurance contributions and irrecoverable VAT) and taxes collected (payments to the government administered through business on those involved in their activity, such as income tax and national insurance contributions) to calculate a total tax footprint for organisations.
References
Department for Business and Trade. (2024a). Business Population Estimates. Available at: www.gov.uk/government/collections/business-population-estimates
Department for Business and Trade. (2024b). Longitudinal Small Business Survey. Available at: www.gov.uk/government/collections/small-business-survey-reports#2023
European Commission. (2009). Overview of Family-Business-Relevant Issues: Research, Networks, Policy Measures and Existing Studies. Directorate-General for Enterprise and Industry. Available at: www.scirp.org/reference/referencespapers?referenceid=2988911
NIESR. (2023). Management and Wellbeing Practices Survey. Available at: www.niesr.ac.uk/projects/management-andwellbeing-practices-survey
Office for National Statistics. (2024). Non-Financial Business Economy, UK: Sections A to S. Available at: www.ons.gov.uk/businessindustryandtrade/business/businessservices/datasets/Uknonfinancialbusinesseconomyannualbusinesssurveysectionsas
PwC/IFB Research Foundation (2023). The Total Tax Contribution of UK Family Businesses. Available at: https://www.fbrf.org.uk/reports/total-tax-contribution-of-uk-family-businesses
RepGraph. (2020). The Largest Family Business in the UK. IFB Research Foundation. Available at: www.fbrf.org.uk/reports/largest-family-firms